TL;DR: Curious about where industrial design is headed in 2025? This guide covers the biggest trends shaping the future of design—including sustainable materials, circular economy principles, minimalist aesthetics, AI-powered design tools, AR/VR prototyping, biophilic inspiration, and emotionally driven experiences. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, engineer, or product designer, these insights will help you stay ahead of evolving consumer expectations and industry innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Sustainable design is key in 2025, focusing on eco-friendly materials and circular economy principles to reduce environmental impact.
- Minimalist aesthetics are trending, emphasizing simplicity, functionality, and visual hierarchy for enhanced user experience.
- AI and advanced manufacturing techniques are transforming industrial design, enabling customization, efficiency, and innovative product development.
- Human-centered design is ensuring that products meet the diverse needs of users, making them more intuitive and inclusive.
Embracing Sustainable Design
Sustainable design is now a cornerstone of modern industrial design. It considers the social, environmental, and economic impacts throughout a product’s lifecycle. This holistic approach leads to reduced environmental impact, enhanced resilience, and long-term cost savings.
Rising consumer awareness and expectations for eco-friendly practices are pushing the trend towards sustainability in product design. Designers are using eco-friendly materials and waste reduction strategies to develop products with a smaller environmental footprint.
Circular Economy
The circular economy is crucial to sustainable design, encouraging recycling, upcycling, and waste reduction. Circular design principles, such as cradle-to-cradle (C2C), prioritize recyclability and reuse, extending the lifespan of materials and products.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Eco-friendly materials are becoming more popular as consumers increasingly seek sustainable products. Industrial designers are exploring innovative materials like compostable substances, recycled plastics, and biodegradable composites. Notable advancements include bio-based plastics made from renewable sources such as seaweed.
Going for Minimalist Aesthetics
Minimalist aesthetics, focusing on eliminating excess to highlight essentials, have become a hallmark of contemporary industrial design. Brands like Muji and Apple effectively use minimalist aesthetics, creating products that are both functional and visually appealing.
The philosophy of ‘less is more’ is more relevant than ever, with designs characterized by clean lines, simplicity, and functionality. Products like the iPhone exemplify this approach, offering a sleek design with minimal features that focus on user experience.
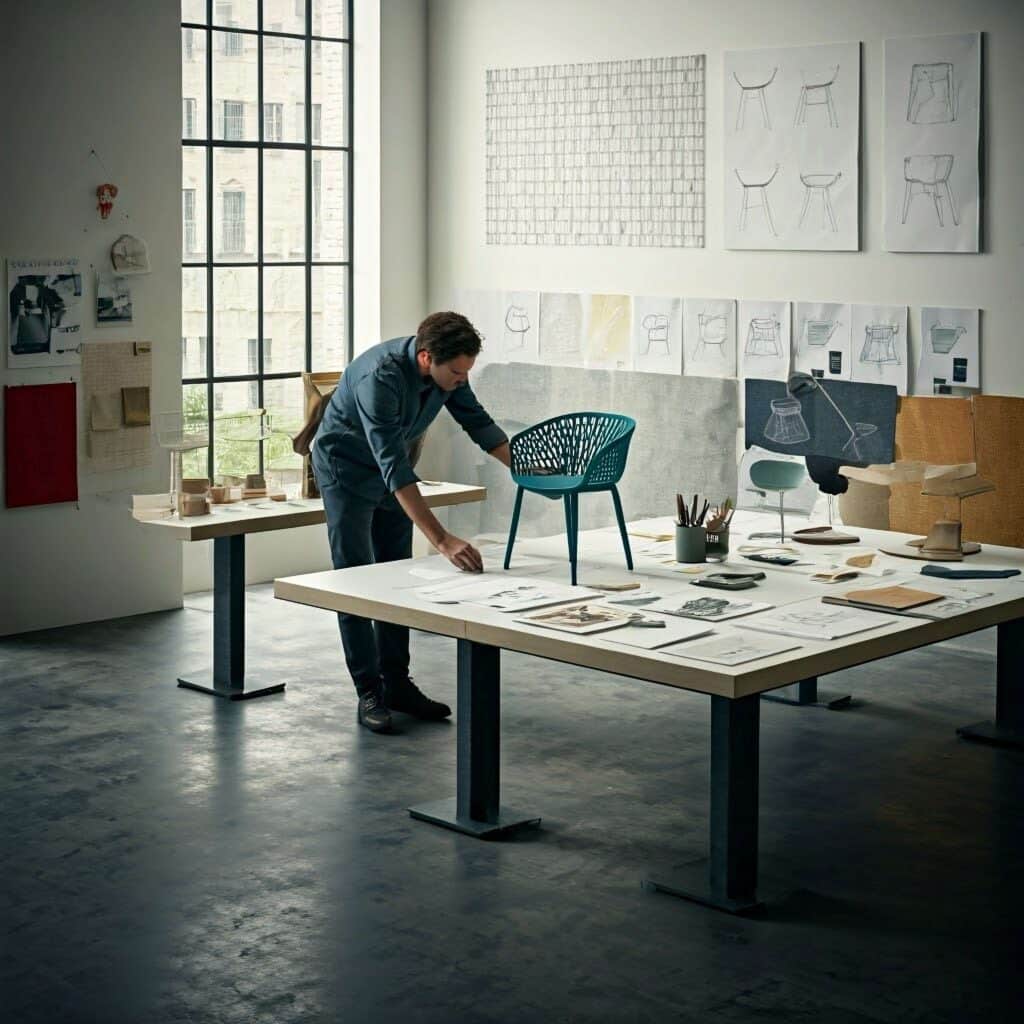

Functional Simplicity
In 2025, designs will prioritize user experience by removing non-essential features. Balancing simplicity and functionality remains a critical challenge, with textures being used to enhance minimalism.
Examples like the KURVE chair, which features a backless box design made from a single sheet of layered plywood, embody the principles of functional simplicity.
Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy plays a key role in minimalist designs, guiding user attention and improving usability. Elements like color, typography, and texture play a crucial role in creating visual appeal and guiding user focus.
For instance, a well-implemented color pop can highlight key features, while dark mode can reduce eye strain and improve usability.

The Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industrial design by transforming how products are conceptualized and developed. AI-powered design tools enable industrial designers to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns in successful designs, and generate innovative solutions that better meet user needs.
AI brings several key advancements to industrial design:
- Rapid prototyping and design iteration
- Material optimization and performance analysis
- Design validation through predictive modeling
- Automated design testing and refinement
- Enhanced ergonomic analysis
Design Optimization
AI systems analyze successful design patterns across industries, helping designers make more informed decisions about form, function, and materials. Advanced algorithms can simulate how different design choices might perform in real-world conditions, reducing the time and resources needed for physical prototyping.
Advanced Design Solutions
AI enhances the industrial design process by identifying optimal solutions for complex design challenges. For example, generative design algorithms can suggest structural improvements while maintaining aesthetic requirements, leading to products that are both beautiful and functional.
Intelligent Manufacturing Integration
The integration of AI in industrial design extends to the manufacturing process, ensuring designs are optimized for production. This technology helps designers create products that are not only innovative but also practical to manufacture at scale, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Advanced manufacturing innovations are transforming the industrial design industry. For example, 3D printing offers cost-effective solutions for producing small batches of specialized products. This technology can utilize a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, textiles, concrete, and glass, broadening design possibilities and facilitating rapid prototyping.
AR/VR solutions enhance manufacturing by improving visualization and detecting design flaws before production. Tools like AR-powered smart glasses overlay 3D models onto physical workspaces, allowing designers to explore and manipulate 3D creations intuitively, enhancing the design experience and reducing errors.
3D Printing Innovations
Recent advancements in 3D printing technology are enabling more intricate and customized designs. This technology supports the use of innovative materials like high-performance alloys and specialized gel-based substances, reshaping structural innovations in industrial design.
Hybrid metal-dielectric 3D printing is improving design space, adhesion quality, and overall efficiency.
Common materials compatible with 3D printers include:
- Plastics
- Metals
- Textiles
- Concrete
- Glass
- High-performance alloys (titanium, aluminum)
- Specialized gels and resins
Digital Fabrication
Digital fabrication technologies, such as laser cutters and robotic arms, enhance manufacturing precision and speed. These tools provide greater accuracy in production processes, reducing human error and material waste.
Platforms like Parallel Pipes facilitate rapid product development with precise intent, streamlining the design process and enabling more efficient, sustainable products.
Biophilic and Bio-Design Trends
Biophilic and bio-design trends are gaining traction as industrial designers seek to integrate natural elements and living organisms into their work.
Biophilic design uses textures, elements, and patterns reflecting nature, enhancing visual appeal and connecting to the natural world. Bio-design incorporates living organisms into the design process to create sustainable, functional products.
These approaches promote sustainability and enhance user well-being and creativity. The growth of biophilic design is influenced by developments in generative and parametric design, which allow designers to draw inspiration from nature and create innovative solutions that resonate with users.
Nature-Inspired Solutions
Designs inspired by nature include elements that connect users to nature, enhancing well-being and creativity. Examples include wood or stone textures, wave-like animations, and tree vine lines.
Brayfoil Technologies, for instance, draws natural inspiration from the efficiency of African birds of prey for its turbine design, showcasing how nature can solve design challenges.
Biomimicry
Biomimicry involves simulating natural characteristics or strategies to solve design challenges. It focuses on nature’s patterns, processes, and strategies, promoting sustainability and resilience.
For instance, self-healing materials mimic natural repair processes, enhancing efficiency and ecological consciousness. Brayfoil Technologies’ morphing wing technology, inspired by nature, improves aerodynamic performance, showcasing the potential of biomimicry in industrial design.
Human-Centered Design
Human-centered design is a significant trend in industrial design that aims to prioritize the needs and experiences of end-users. A deep understanding of user needs allows designers to create intuitive, inclusive, and satisfying products. This approach plays a crucial role in product development, ensuring that user needs are prioritized and leading to more effective and efficient solutions.
The human-centered design process involves stages such as observing the problem, brainstorming solutions, and implementing user-testing methodologies. User-centric analytics inform design decisions, shorten development cycles, and increase user adoption, creating solutions that resonate with consumers.

User Research
User research is crucial to human-centered design, providing early insights in the design process. Methods like empathy mapping and testing are vital for understanding user needs and preferences.
Platforms like Maze offer designers deep insights, helping them create user-friendly products that meet expectations.
Inclusive Design
Inclusive design aims to ensure full participation of people with disabilities and marginalized groups. Unlike accessible design, which focuses on usability for individuals with varying abilities, inclusive design accounts for diversity in gender, race, age, ethnicity, and sexual orientation.
When we look at examples like the “Inclusivitea” kettle, its redesigned handle and brewing stand demonstrate how inclusive design can enhance usability and expand the customer base, helping make people’s day-to-day lives better. By simply featuring two horizontal handles, it made a world of difference in useability for people of all strength and dexterity levels.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are revolutionizing industrial design by enhancing visualization and collaboration. These technologies provide designers and stakeholders with virtual prototypes, improving understanding and reducing the risk of design flaws.
Products like the Sirius smart goggles integrate AR and AI to deliver crucial information, showcasing the capabilities of these technologies in specific applications.
Emerging technologies like quantum computing and augmented intelligence are also significantly impacting industrial design, alongside AR and VR. These technological advancements enable designers to intuitively explore and manipulate 3D creations in new ways.
Immersive Experience
Augmented reality provides immersive experiences that boost user confidence and reduce product returns by allowing product visualization before purchase. AR-powered tools let designers overlay digital models onto real-world environments, enhancing interaction and product fit.
This technology bridges the gap between product design and user experience, leading to greater satisfaction and reduced returns.
Enhanced Collaboration
AR and VR enhance collaboration among design teams by improving communication and interaction with design concepts. These tools enable inspection teams to overlay digital information onto physical objects in real-time, improving accuracy in the design process.
This integration results in enhanced collaborative efforts, streamlining the design process and improving the quality of the end product.
Emotional and Narrative-Driven Design
Emotional and narrative-driven design aims to create products that users feel a personal connection with. Designing with the user’s emotions in mind allows industrial designers to create experiences that evoke positive emotions and build brand loyalty. Creating a design narrative aims to connect emotionally with customers, enhancing user engagement and fostering meaningful interactions.
Brands like Patagonia showcase effective design narrative by integrating sustainability into every design, resonating with buyers’ values. This approach not only enhances user interaction but also reinforces the brand’s commitment to sustainability, creating a deeper connection with consumers.
Storytelling in Design
Storytelling in design connects brands with their audience by communicating values and narratives. Effective storytelling boosts user engagement, enabling consumers to form emotional connections with products. This fosters meaningful user experiences that can lead to brand loyalty and a deeper connection with users.
Emotional Design Elements
Incorporating emotional design elements is key to creating user experiences that meet functional needs and forge emotional connections. Emotion-evoking design elements enhance user interaction, leading to greater product attachment and brand loyalty.
Modular and Customizable Products
The industrial design landscape is seeing a significant shift towards modularity and customization. This trend reflects a growing consumer desire for products that can be tailored to individual needs and preferences. Modular design enables products to be reconfigured or expanded, providing unmatched flexibility and adaptability to meet diverse user needs.
Adaptable Solutions
Customizable products are gaining traction across various industries, from furniture to electronics. These designs allow consumers to make choices in colors, materials, and features, creating a more personalized user experience. For instance, modular smartphones enable users to upgrade specific components rather than replacing the entire device, reducing electronic waste and extending product lifespan.
Sustainable Modularity
This trend not only caters to consumer preferences but also aligns with sustainability goals. Modular designs often result in easier repairs and upgrades, potentially reducing overall consumption and waste.
Companies like Framework are pioneering this approach with laptops designed for easy user upgrades and repairs, showcasing how modularity can enhance both user experience and product longevity.
Industrial 2.0 Design
Industrial 2.0 design represents an evolution of the traditional industrial style, pushing boundaries and redefining aesthetic norms. This trend is characterized by a raw and hard aesthetic that focuses on contrasts, incorporating elements from various design philosophies such as new brutalism, wabi-sabi, and upcycling.
Material Innovation
The use of materials plays a crucial role in Industrial 2.0 design. Aluminum and recycled plastics are gaining popularity, offering both durability and sustainability. These materials are often left exposed, celebrating their inherent properties and imperfections.
Upcycled Aesthetics
Industrial 2.0 also embraces the concept of upcycling, giving new life to discarded materials and objects. Designers are repurposing industrial components and machinery parts into functional art pieces and furniture, blurring the lines between industrial remnants and high-end design.
Sleek and Ergonomic Design
Ergonomics is taking center stage in industrial design. The focus is on creating products that are not just visually appealing but also comfortable and easy to use. This trend is particularly evident in everyday tools and tech gadgets where user comfort is paramount.
Human-Centered Comfort
Designers are paying close attention to the human body’s natural movements and limitations, creating products that reduce strain and enhance usability. Office chairs are being redesigned with ergonomic principles in mind, featuring adjustable lumbar support and contours that encourage proper posture.
Form Meets Function
The integration of sleek aesthetics with ergonomic functionality is challenging designers to think creatively. The result is a new generation of products that seamlessly blend form and function, offering users both visual appeal and physical comfort.
The Future of Industrial Design
Looking ahead, industrial design is being driven by a wave of innovation and creativity. Sustainable practices, minimalist aesthetics, AI, advanced manufacturing, biophilic influences, and human-centered approaches are transforming the landscape. Technologies like AR and VR, along with emotionally driven design elements, are enhancing user experience in profound ways.
For those involved in industrial design, staying informed on these trends is essential as they shape the path forward for the industry, ensuring products that are not only functional but also emotionally engaging and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the circular economy, and how does it relate to industrial design?
The circular economy is all about recycling and reducing waste to extend the life of materials and products. In industrial design, it means crafting items that are easy to recycle and reuse, helping us move toward a more sustainable future.
How are eco-friendly materials being used in product design?
Eco-friendly materials are becoming a staple in product design, with designers using compostable substances, recycled plastics, and biodegradable composites. This shift not only minimizes waste but also paves the way for innovative solutions like bio-based plastics from renewable resources.
What role does AI play in personalized product design?
AI plays a crucial role in personalized product design by learning from user interactions to create customized products that cater to individual preferences.
How do AR and VR technologies enhance the design process?
AR and VR technologies really elevate the design process by allowing designers to create virtual prototypes that improve visualization and collaboration. With the ability to overlay digital information on physical objects in real-time, communication becomes clearer, leading to greater accuracy in design.
What is human-centered design, and why is it important?
Human-centered design focuses on the needs and experiences of users to create intuitive and inclusive products. It’s important because it leads to solutions that are more effective and satisfying for the end-user.



