The manufacturing landscape is evolving at breakneck speed, driven by technological advancements and global shifts. As we look ahead to 2025, the industry is poised for remarkable transformation. Despite challenges in recent years, including the aftermath of the pandemic and ongoing geopolitical tensions, the sector is showing resilience with a projected annual growth rate of 3.57% through 2028.
In this deep dive, we’ll explore the top trends reshaping manufacturing in 2025. From the rise of digital twins to the pressing need for cybersecurity, we’ll unpack what these changes mean for your business and how you can stay ahead of the curve.
Key Takeaways
- Digital transformation is reshaping manufacturing, with smart factories, AI, and digital twins driving efficiency and predictive maintenance.
- Supply chain resilience and sustainability are becoming critical, accelerating reshoring efforts and pushing towards carbon neutrality.
- The workforce is evolving, with manufacturers addressing skills gaps through reskilling initiatives and adopting new technologies like robotics and AR/VR.
- Economic pressures and cybersecurity threats are prompting manufacturers to focus on operational efficiency and robust digital defenses.
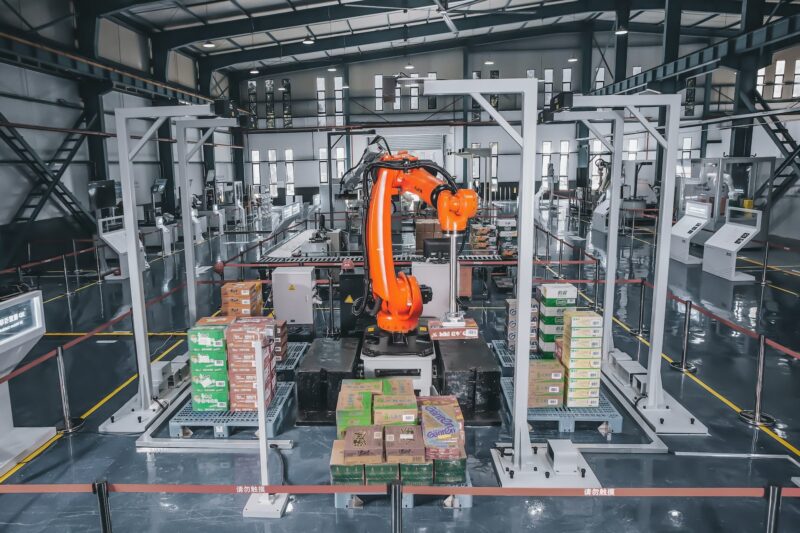
1. Smart Factories are Transforming Operations and Shop Floors
Remember when smartphones revolutionized communication? Well, smart factories are doing the same for manufacturing. These highly automated facilities are the beating heart of Industry 4.0, leveraging cutting-edge technologies to streamline operations and boost efficiency.
The Smart Factory Boom
The numbers don’t lie – the global smart factory market is on a tear, expected to reach a staggering $321.98 billion by 2032. That’s a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.52%! But what’s driving this explosive growth?
- AI and IoT Integration: Smart factories are harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things to create interconnected systems that can think and adapt in real-time.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: With sensors collecting data at every stage of production, manufacturers can make informed decisions faster than ever before.
- Automated Quality Control: AI-powered systems can spot defects with superhuman accuracy, ensuring consistently high-quality outputs.
Real-World Impact
Let’s look at how this is playing out in the real world. Siemens, a trailblazer in smart manufacturing, has implemented fully automated and connected factories across its global network. The result? Optimized production, fewer errors, and a leaner, more efficient operation.
But it’s not just the big players benefiting. Small and medium-sized manufacturers are also getting in on the action, using modular smart factory solutions to boost their competitiveness.
What This Means for You
If you’re not already thinking about how to smarten up your manufacturing processes, now’s the time to start. The initial investment might seem daunting, but the long-term benefits – improved quality, increased efficiency, and reduced waste – are too significant to ignore.
2. Artificial Intelligence is Driving Smarter Manufacturing
Artificial Intelligence isn’t just changing the game; it’s rewriting the rulebook entirely. In 2025, AI will be the invisible force driving smarter decision-making, predictive maintenance, and hyper-optimized supply chains.
AI’s Growing Footprint
The manufacturing sector is rapidly embracing AI, with adoption rates soaring. Here’s what’s fueling this trend:
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can forecast everything from equipment failures to market demands, allowing manufacturers to stay one step ahead.
- Quality Assurance: AI-powered visual inspection systems can detect defects faster and more accurately than human inspectors, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI helps manage complex global supply networks, providing real-time insights and allowing for quick responses to disruptions.
The Human Touch in an AI World
But don’t worry – AI isn’t here to replace humans. Instead, it’s augmenting human capabilities, allowing workers to focus on more strategic, creative tasks. As one manufacturing executive put it, “AI handles the data crunching, so our team can focus on innovation and problem-solving.”
Embracing AI: A Competitive Necessity
For manufacturers looking to scale efficiently and stay competitive, AI is no longer optional – it’s essential. Early adopters are already seeing significant returns in terms of cost reduction, quality improvement, and increased agility.
3. Digital Twins and Predictive Maintenance are Enabling Better Decision-Making
Imagine having a crystal ball that could predict when your equipment will fail before it happens. That’s essentially what digital twins and predictive maintenance offer manufacturers in 2025.
The Rise of Digital Doppelgangers
Digital twin technology – virtual replicas of physical assets or processes – is revolutionizing how manufacturers operate and maintain their equipment. The market for this tech is booming, expected to reach $73.5 billion by 2027. But what’s driving this growth?
- Real-Time Monitoring: Digital twins provide a live, data-driven view of equipment performance, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Scenario Testing: Manufacturers can simulate various conditions and scenarios without risking actual equipment, leading to better decision-making.
- Lifecycle Management: From design to decommissioning, digital twins offer insights at every stage of an asset’s life cycle.
Predictive Maintenance: A Game-Changer
Paired with digital twins, predictive maintenance is helping manufacturers say goodbye to unexpected downtime. The numbers speak for themselves:
- 40% reduction in maintenance costs
- 70% decrease in breakdowns
- 25-30% increase in overall equipment effectiveness
Real-World Application
General Electric (GE) has been a pioneer in leveraging digital twin technology. By creating virtual replicas of their jet engines, GE can simulate performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize the entire product lifecycle. The result? Happier customers, lower costs, and more efficient operations.
Your Path to Predictive Power
Implementing digital twins and predictive maintenance might seem like a big leap, but the potential returns make it worth considering. Start small – perhaps with your most critical equipment – and scale up as you see results. Remember, the most successful manufacturers will be those who can predict and prevent issues before they occur.
4. Supply Chain Challenges are Accelerating Reshoring Efforts
The global events of recent years have exposed the vulnerabilities in our interconnected supply chains. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly looking to bring production closer to home – a trend known as reshoring, though cost considerations remain a significant factor in this decision.
The Reshoring Revolution
The numbers are striking: over 364,000 jobs were reshored in 2022 alone, according to The Reshoring Initiative. But why the sudden shift?
- Risk Mitigation: Shorter supply chains mean less exposure to global disruptions.
- Quality Control: Closer proximity allows for better oversight and quicker problem-solving.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Reduced lead time and shipping distances mean products can reach customers more quickly.
Benefits Beyond the Bottom Line
Reshoring isn’t just about reducing risks; it’s about creating opportunities:
- Local Economic Boost: Domestic manufacturing creates jobs and stimulates local economies.
- Innovation Hubs: Proximity between R&D and production can accelerate innovation cycles.
- Sustainability: Shorter supply chains often mean a reduced carbon footprint.
Real-World Reshoring
Take Tesla, for example. By producing vehicles closer to their main markets, they’ve not only reduced logistics costs but also gained more control over their production process. Similarly, when Apple moved some of its production back to the U.S., they were able to implement tighter quality control measures.
Is Reshoring Right for You?
While the benefits are clear, reshoring isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It requires careful consideration of factors like labor costs, skill availability, and infrastructure. For many US-based companies, particularly those operating at smaller scales, the higher labor and operational costs of domestic manufacturing often make reshoring financially unfeasible despite its potential benefits. The decision to reshore must be evaluated against these significant cost implications, especially when competing in price-sensitive markets.
5. Sustainability is Pushing Manufacturing Toward Carbon Neutrality
In 2025, sustainability isn’t just a buzzword – it’s a business imperative. With one-fifth of global carbon emissions coming from the manufacturing sector, the industry is under increasing pressure to clean up its act.
The Push for Carbon Neutrality
Many Fortune Global 500 companies are leading the charge, pledging to achieve carbon neutrality by 2030. But what’s driving this green revolution?
- Consumer Demand: Eco-conscious consumers are voting with their wallets, favoring brands with strong sustainability credentials.
- Regulatory Pressure: Governments worldwide are tightening environmental regulations, making sustainability a compliance issue.
- Cost Savings: Surprisingly, going green often leads to significant cost reductions in the long run.
Sustainability Success Stories
Let’s look at some companies that are walking the talk:
- Patagonia: This outdoor clothing company has built its brand around environmental stewardship, proving that sustainability and profitability can go hand in hand.
- Interface: This flooring manufacturer cut its carbon emissions by a whopping 96%, all while reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Unilever: By aligning its products with eco-friendly values, Unilever has seen increased market share in emerging markets where sustainability is a priority.
Your Green Manufacturing Roadmap
So, how can you join the sustainability revolution? Here are some steps to consider:
- Energy Efficiency: Invest in energy-efficient machinery and processes.
- Renewable Energy: Consider on-site renewable energy generation or purchasing green energy.
- Circular Economy: Look for ways to reduce waste and reuse materials in your production process.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Work with suppliers who share your commitment to sustainability.
Remember, being green isn’t just good for the planet – it’s good for business too.
6. Workforce Evolution is Addressing the Skills Gap
The manufacturing industry faces a pressing challenge: a widening skills gap. With an estimated 2.1 million jobs potentially going unfilled by 2030, manufacturers need to get creative about attracting and retaining talent.
The Talent Crunch
The numbers are sobering:
- Potential loss of up to $1 trillion in revenue due to unfilled jobs
- 75% of manufacturers reporting difficulties in attracting and retaining workers
But why is this labor shortage happening? A combination of factors is at play:
- An aging workforce with experienced workers retiring
- Rapid technological advancements creating demand for new skills
- Misconceptions about manufacturing careers among younger generations
Strategies for Success
Forward-thinking manufacturers are tackling this challenge head-on. Here’s how:
- Competitive Wages: Nearly three-quarters of manufacturers plan to raise wages by 3% or more to attract skilled workers.
- Reskilling and Upskilling: Companies are investing heavily in training programs to equip their existing workforce with the skills needed for the future of manufacturing.
- Partnerships with Educational Institutions: Many manufacturers are collaborating with local schools and colleges to create tailored curricula that prepare students for careers in modern manufacturing.
- Embracing Diversity: Expanding recruitment efforts to underrepresented groups can help broaden the talent pool.
- Improving Work Environment: From flexible schedules to career development opportunities, companies are focusing on creating more appealing workplaces.
The Human Touch in a Digital World
While automation and AI are reshaping manufacturing, human skills remain crucial. As one industry leader put it, “There’s no such thing as a low-skilled job in manufacturing anymore. We need people who can work with advanced technologies, problem-solve, and innovate.”
Your Workforce Strategy for 2025
As you plan for the future, consider these questions:
- How can you make your company more attractive to the next generation of manufacturing talent?
- What skills will your workforce need in 2025 and beyond?
- How can you create a culture of continuous learning and development?
Remember, in the race for talent, the manufacturers who invest in their people today will be the winners of tomorrow.
7. Cybersecurity Threats are Reshaping Manufacturing Defenses
As manufacturing becomes increasingly digitized, cybersecurity is no longer just an IT issue – it’s a core business concern. Protecting your digital assets will be just as crucial as safeguarding your physical ones.
The Growing Threat Landscape
The numbers are alarming:
- 53% increase in cyber-attacks on the manufacturing sector year-over-year
- Manufacturing is now one of the most targeted industries by cybercriminals
Why? The rise of smart factories, IoT devices, and interconnected systems has created new vulnerabilities that hackers are all too eager to exploit.
Types of Threats
Manufacturers face a range of cyber threats:
- Ransomware: Malicious software that locks companies out of their systems, demanding payment for release.
- Industrial Espionage: Attempts to steal valuable intellectual property or trade secrets.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting vulnerabilities in the supply chain to gain access to larger systems.
- Operational Disruption: Attacks aimed at halting production or causing physical damage to equipment.
Building Your Cyber Defenses
So, how can manufacturers protect themselves? Here are some key strategies:
- Multi-layered Security: Implement a comprehensive security approach that includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
- Employee Training: Your workforce is your first line of defense. Regular cybersecurity training is crucial.
- Secure-by-Design: Integrate security considerations into the design of your systems and processes from the ground up.
- AI-Driven Threat Detection: Leverage artificial intelligence to identify and respond to threats in real-time.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Keep all systems and software up-to-date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Case Study: Siemens’ Cybersecurity Approach
Siemens, a leader in smart manufacturing, has made cybersecurity a core part of its digital strategy. They’ve implemented a “defense in depth” approach, which includes:
- Secure network architecture
- System hardening
- Access control and user authentication
- Continuous monitoring and incident response
The result? A more resilient and trustworthy manufacturing ecosystem.
Your Cybersecurity Roadmap
As you prepare for 2025, consider these questions:
- How vulnerable are your current systems to cyber attacks?
- Do you have a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy in place?
- Are your employees trained to recognize and respond to cyber threats?
Remember, in the digital age, cybersecurity isn’t just about protecting data – it’s about ensuring the continuity and integrity of your entire manufacturing operation.
8. Economic Pressures are Driving Operational Efficiency
Manufacturers face a complex economic landscape in 2025. From inflation and rising interest rates to ongoing supply chain disruptions, the challenges are multifaceted. But with challenge comes opportunity, and forward-thinking manufacturers are finding innovative ways to navigate these turbulent waters.
The Economic Outlook
Let’s break down the key economic factors impacting manufacturing:
- Inflation: Rising costs for materials and energy are squeezing profit margins.
- Interest Rates: Higher borrowing costs are making it more expensive to finance new projects and expansions.
- Supply Chain Volatility: Ongoing disruptions are forcing manufacturers to rethink their supply strategies.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes add an extra layer of complexity to business planning.
Strategies for Success
So, how are savvy manufacturers responding to these pressures? Here are some key approaches:
- Operational Efficiency: Companies are doubling down on lean manufacturing principles, using technologies like AI and IoT to optimize processes and reduce waste.
- Diversification: Many manufacturers are diversifying their product lines and target markets to spread risk and capture new opportunities.
- Agile Planning: Short-term planning cycles and scenario-based forecasting are helping companies stay nimble in an unpredictable environment.
- Strategic Investments: Despite economic pressures, manufacturers are still investing in key areas like automation and sustainability, recognizing their long-term value.
- Pricing Strategies: Some companies are exploring dynamic pricing models to better manage fluctuating costs and demand.
Case Study: Adapting to Economic Pressures
Take the example of a mid-sized automotive parts manufacturer. Faced with rising material costs and supply chain disruptions, they:
- Implemented an AI-driven inventory management system to optimize stock levels
- Invested in local suppliers to reduce reliance on global supply chains
- Developed a modular product design that allowed for easier adaptation to changing market demands
The result? Improved resilience, reduced costs, and the ability to maintain competitive pricing despite economic headwinds.
Your Economic Strategy for 2025
Consider these questions while planning your economic strategy:
- How can you increase your operational efficiency to offset rising costs?
- Are there opportunities to diversify your product line or target markets?
- How can you make your supply chain more resilient to global disruptions?
- What strategic investments will position you for long-term success, even in a challenging economic environment?
Remember, while economic pressures pose significant challenges, they also create opportunities for innovation and differentiation. The manufacturers who can adapt and optimize in the face of these pressures will be the ones who thrive in the future.
9. Robotics and Automation are Redefining the Manufacturing Workforce
The integration of robotics and automation in manufacturing is accelerating at an unprecedented pace. These technologies are no longer confined to repetitive tasks; today’s advanced machines are capable of handling complex operations, making production lines faster, more accurate, and infinitely more flexible.
The Robot Revolution
The numbers tell a compelling story:
- The global industrial robotics market is projected to reach $81.4 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 11.8%
- Collaborative robots (cobots) are expected to see even faster growth, with a CAGR of 32.5% through 2030
Beyond the Assembly Line
Today’s robots are far more sophisticated than their predecessors. Here’s how they’re transforming manufacturing:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): These machines work alongside humans, enhancing productivity and safety. They’re particularly useful for tasks that require a combination of precision and flexibility.
- Mobile Robots: Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are revolutionizing material handling and inventory management, navigating factory floors with ease.
- AI-Powered Robots: Combining robotics with artificial intelligence creates machines that can learn and adapt, handling increasingly complex tasks.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): This software-based automation is streamlining back-office processes, from order processing to quality control documentation.
The Human-Robot Synergy
Contrary to popular belief, the rise of robotics doesn’t necessarily mean fewer jobs for humans. Instead, it’s changing the nature of work in manufacturing. As robots take over repetitive and dangerous tasks, human workers are freed up to focus on more strategic, creative, and value-added activities.
Case Study: FANUC’s Lights-Out Manufacturing
FANUC, a leading robotics manufacturer, has implemented a “lights-out” factory in Japan. This facility can run unattended for up to 30 days at a time, with robots building other robots. The result? Dramatically increased productivity and consistency, with human workers focusing on programming, maintenance, and continuous improvement.
Implementing Robotics: A Roadmap
If you’re considering ramping up your robotics and automation efforts, here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Assess Your Needs: Identify areas where automation could have the biggest impact on productivity and quality.
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot project to prove the concept and gain buy-in from stakeholders.
- Invest in Training: Ensure your workforce has the skills to work alongside and maintain robotic systems.
- Plan for Integration: Consider how robotics will integrate with your existing systems and processes.
- Measure and Optimize: Continuously monitor performance and look for opportunities to improve and expand your robotics initiatives.
The Future is Collaborative
The most successful manufacturers will be those who find the right balance between human skills and robotic efficiency. It’s not about replacing humans with robots, but about creating a synergy that enhances overall productivity and innovation.
10. Immersive Technologies Are Transforming Training and Design
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are moving beyond gaming and entertainment to transform core aspects of manufacturing. These immersive technologies are reshaping everything from product design to employee training, offering unprecedented levels of visualization and interaction.
The AR/VR Market Boom
The numbers speak volumes:
- The global AR market in manufacturing is projected to reach $19.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 46.4%
- VR in manufacturing is expected to hit $14.1 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 39.2%
Transforming Manufacturing Processes
Let’s dive into how AR and VR are revolutionizing different aspects of manufacturing:
Product Design and Prototyping
VR allows designers to create and manipulate 3D models in a virtual space, speeding up the design process and reducing the need for physical prototypes. This not only saves time and materials but also allows for more iterations and improvements before production begins.
Automotive giant Ford uses VR to design and test vehicle prototypes, allowing engineers to make changes and improvements without building costly physical models.
Employee Training
AR and VR provide immersive, hands-on training experiences without the risks associated with real-world training on expensive or dangerous equipment.
Boeing uses AR headsets to guide technicians through complex wiring assemblies, reducing error rates by 90% and improving productivity by 30%.
Maintenance and Repairs
AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, assisting technicians with maintenance and repair tasks. This can significantly reduce downtime and improve accuracy.
Thyssenkrupp uses Microsoft HoloLens to help elevator service technicians visualize and identify problems, resulting in a four-fold increase in efficiency.
Quality Control
AR can superimpose design specifications or quality benchmarks onto physical products, making it easier for workers to spot defects or deviations.
Remote Collaboration
VR enables teams in different locations to collaborate in a shared virtual space, improving communication and problem-solving across global operations.
Implementing AR/VR: Best Practices
If you’re considering integrating AR or VR into your manufacturing processes, here are some tips:
- Identify High-Impact Areas: Focus on processes where visualization and immersion can provide the most significant benefits.
- Start with Pilot Projects: Begin with small-scale implementations to prove value and gain organizational buy-in.
- Prioritize User Experience: Ensure the technology is intuitive and adds value to users’ work, rather than complicating it.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Look for AR/VR solutions that can integrate seamlessly with your current software and data systems.
- Invest in Training: Ensure your team is comfortable and proficient with the new technology.
The Future is Immersive
AR and VR will increasingly blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds in manufacturing. These technologies offer the potential to dramatically improve efficiency, quality, and innovation across the entire manufacturing value chain.
By embracing these immersive technologies, manufacturers can gain a significant competitive edge, creating more efficient processes, better products, and a more skilled and engaged workforce.
Embracing the Manufacturing Revolution
As we’ve explored these ten transformative trends, one thing becomes clear: the future of manufacturing is dynamic, digital, and full of opportunity. From smart factories and AI-driven processes to the rise of immersive technologies and sustainable practices, the manufacturing landscape of 2025 will look dramatically different from today’s.
But with great change comes great responsibility. As leaders in the manufacturing industry, it’s up to you to navigate these trends and position your organization for success. Here are some key takeaways to guide your journey:
- Embrace Digital Transformation: The future is digital. Invest in technologies like AI, IoT, and digital twins to stay competitive.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Green manufacturing isn’t just good for the planet; it’s good for business. Make sustainability a core part of your strategy.
- Invest in Your Workforce: The skills gap is real. Focus on attracting, retaining, and upskilling talent to meet the demands of modern manufacturing.
- Build Resilient Supply Chains: Consider reshoring or nearshoring to reduce risks and increase agility.
- Secure Your Digital Assets: As manufacturing becomes more connected, cybersecurity becomes crucial. Make it a top priority.
- Leverage Immersive Technologies: AR and VR offer new ways to design, train, and maintain. Explore how these technologies can benefit your operations.
- Stay Agile: In a rapidly changing environment, the ability to adapt quickly is key. Build flexibility into your processes and mindset.
Remember, the future of manufacturing belongs to those who are willing to innovate, adapt, and lead. By staying informed about these trends and taking proactive steps to implement them, you can position your organization at the forefront of the manufacturing revolution.
The manufacturing industry of 2025 will be smarter, more sustainable, and more connected than ever before. Are you ready to be part of this exciting future?
Frequently Asked Questions
How are smart factories changing the manufacturing landscape?
Smart factories are revolutionizing manufacturing by integrating AI, IoT, and data analytics to create highly automated, efficient operations. They’re enabling real-time decision-making, improving product quality, and increasing overall productivity. With the smart factory market expected to reach $321.98 billion by 2032, this trend is reshaping the entire industry.
What role does AI play in modern manufacturing?
AI is becoming the backbone of smart manufacturing. It’s driving predictive maintenance, optimizing supply chains, and enhancing quality control. AI algorithms can forecast equipment failures, predict market demands, and detect product defects with superhuman accuracy. For manufacturers looking to stay competitive, AI adoption is no longer optional – it’s essential.
How is reshoring impacting the manufacturing sector?
Reshoring is gaining momentum as manufacturers seek to build more resilient supply chains. Over 364,000 jobs were reshored in 2022 alone. This trend is reducing risks associated with global disruptions, improving quality control, and accelerating time-to-market. While not a one-size-fits-all solution, reshoring is helping many companies enhance their competitiveness and agility.
What strategies are manufacturers using to address the skills gap?
With 2.1 million manufacturing jobs potentially going unfilled by 2030, companies are getting creative. They’re raising wages, investing in reskilling and upskilling programs, partnering with educational institutions, and creating more appealing work environments. Many are also leveraging technologies like AR and VR for more effective training. The key is to create a culture of continuous learning and development.
How are economic pressures influencing manufacturing strategies?
Economic challenges are pushing manufacturers to focus on operational efficiency and agility. Companies are adopting lean principles, leveraging AI and IoT for process optimization, diversifying product lines, and implementing more flexible planning cycles. Some are exploring dynamic pricing models to manage fluctuating costs. While these pressures pose challenges, they’re also driving innovation and differentiation in the industry.



